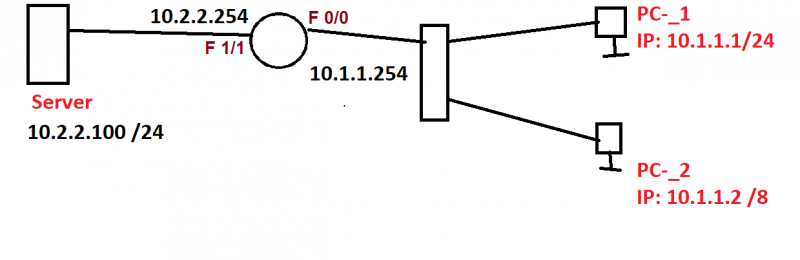
Take a close at the hosts you can see that PC1 has a /24 subnet mask & PC2 has a /8 subnet mask. When PC1 tries to reach the server at 10.2.2.100 the following will happen.
PC1> ping 10.2.2.200
· PC1 perform AND operation to the destination (10.2.2.100) and decides that the server is in another subnet.
· PC1 decides to send the packets towards its default gateway (10.1.1.254).
· PC1 checks its ARP table to see if there is an entry for 10.1.1.254, if does not find & sends an ARP request.
· The router responds to the ARP request which is sent by PC1, sending its MAC address of its interface fast-Ethernet 0/0.
This is how ARP works normally, when PC2 tries to send an IP packet towards the server something else will happen:
PC2> ping 10.2.2.100
· PC2 performs AND operation to the IP address of the server(10.2.2.100) and decides that the server is in the same subnet.
· PC2 will send an ARP request if there is no entry for 10.2.2.100. PC2 does not send ARP request for the gateway.
The server however is not on the same subnet (10.1.1.0 /24) & router do not forward broadcast traffic. Hence, ARP request never make it to the server.
So, this is where proxy ARP comes to the rescue !
· The router sees the ARP request from PC2 on the F 0/0 interface & sees that this is an ARP request for some device in the 10.2.2.0 /24 subnet on F1/1 interface.
· Because directly connected route is present in the Routing table, then router realizes that it knows how to reach the 10.2.2.0 /24 subnet(Server 10.2.2.100) & decides to respond to the ARP request in order to help PC-2.
· The router sends an ARP reply to PC2 with MAC address of the Fast-Ethernet 0/0 interface.
In this way, communication is successful between PC-2 & Server.
Hope this post will be helpful to you. Please ask questions for further clarification.
- How can you guarantee a job for students who has no experience in Networking field?
- How to configure VPN between Cisco Router and ASA Firewall?
- How to configure RIPV2 with no auto summary?
- How to configure PAT (Port Address Translation)?
- How to configure Default Routing on Cisco Routers?
- What is the scope of CCNA course in India?
- What is scope of CCIE?
- How to remember 7 layers of OSI Model?
- How much salary can we get after doing CCNA course in Delhi Gurgaon?
- How many CCIE’s are there worldwide?
- Is it possible to pass CCIE Certification in 1st attempt?






